
a black and white photo of a wolf with trees in the background
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community.. thereafter, a deer would take 10 J (10% of energy) from the plant. A wolf eating the deer would only take 1 J (10% of energy from deer). A human eating the wolf would take 0.1J (10% of energy from wolf), etc..
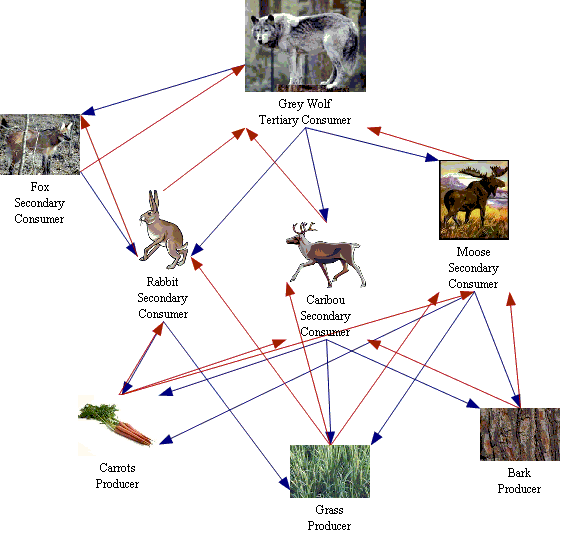
The Grey Wolf's Food Species Survival Guide
The Arctic wolf is a carnivore and is known as a tertiary consumer. This means that they exist in the top level in a food chain. An example of an animal that is beneath the Arctic wolf on the food chain would be the caribou, which is one of its most hunted food sources. As plants are known as the producers, they exist at the bottom of the food.

Citizen scientists help spot 1st ‘wolfdog’ in Pune. Why it’s bad for
Introduction. Food web is an important ecological concept. Basically, food web represents feeding relationships within a community (Smith and Smith 2009). It also implies the transfer of food.

7* Sara C. The Effect of the Reintroduction of Wolves on Yellowstone
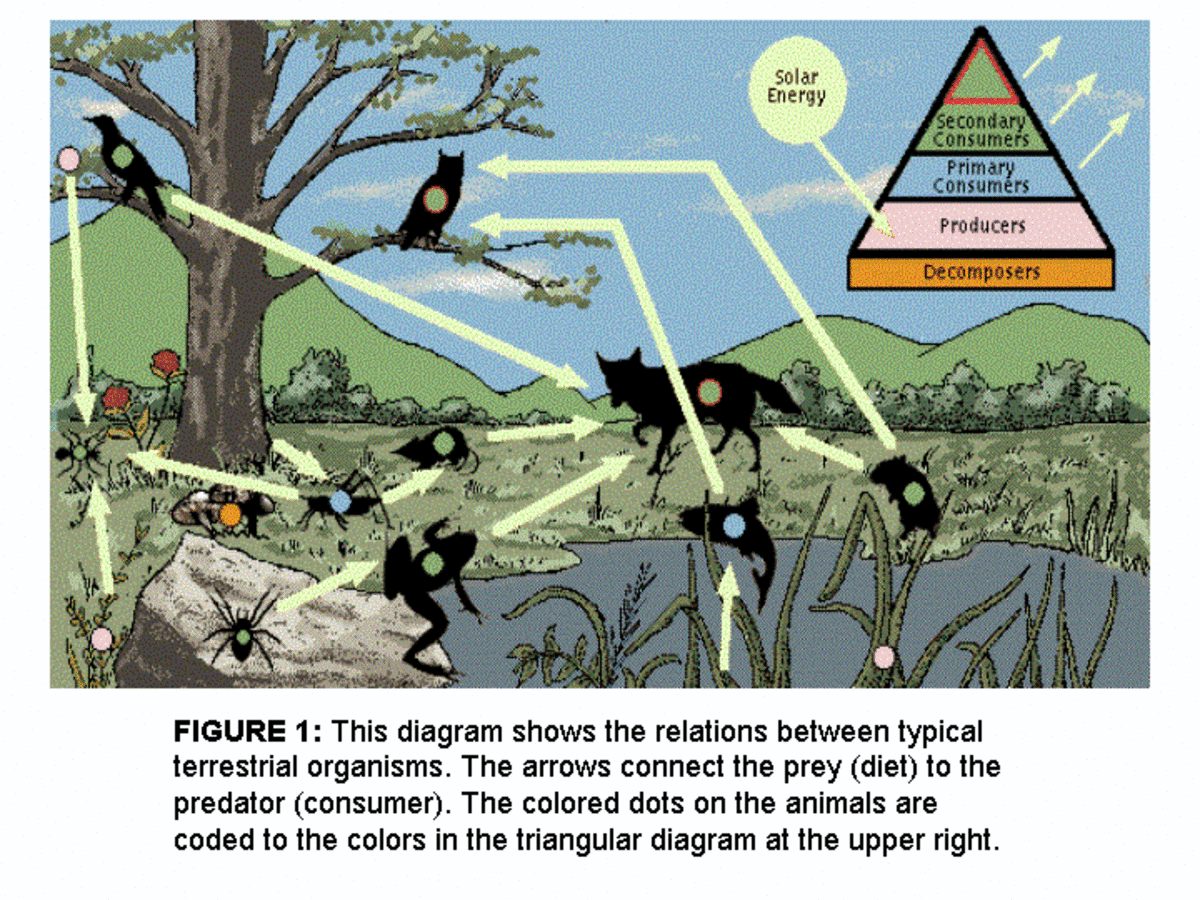
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. Let's look at the parts of a typical food chain, starting from the bottom (the producers) and moving upward. At the base of the food chain lie the primary producers.
Who's Afraid of the Big Bad Wolf? HubPages
Wolves mainly eat meat; they are opportunistic carnivores, meaning they will eat a variety of prey animals depending on what is available to them. Most wolves prefer ungulates, which are large hoofed animals such as deer, bison, elk, and moose. They will also eat smaller mammals such as hares and rabbits, beavers, raccoons, and rodents.

Wolf Drawing by Zakraart. Master of wolfs ARTWOONZ Wolf drawing
Food Chains and Food Webs. In ecology, a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass: primary producers, primary consumers, and higher-level consumers are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. There is a single path through the chain. Food chains do not accurately describe most ecosystems. Even when all organisms are grouped into.
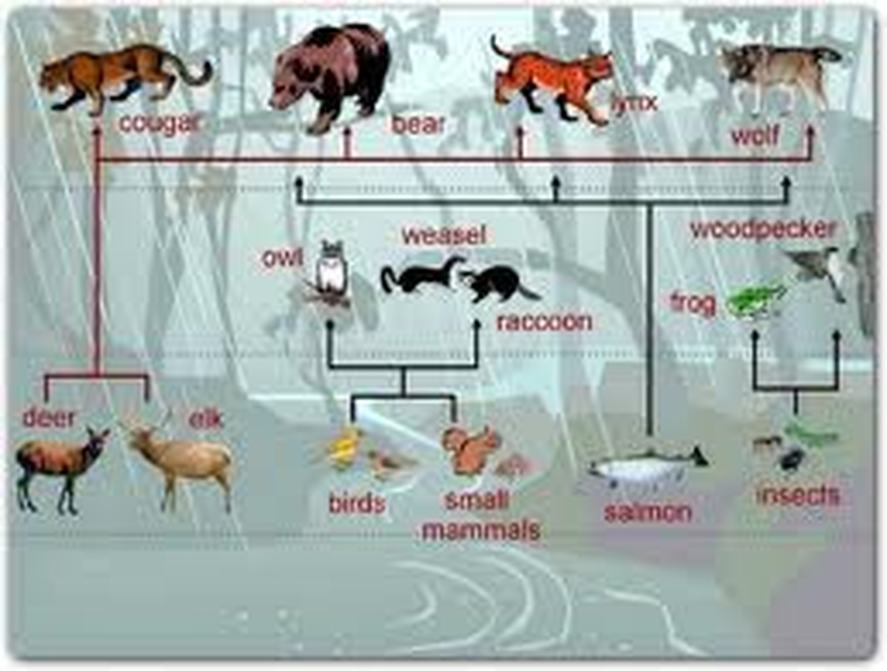
Food web Red Wolf info
In the 1920s, ecologist Charles Elton linked wolf ( Canis lupus) presence to food web effects that can release plants from ungulate herbivory (Elton, 1926). More recently, these food web relationships have been linked to aspen conservation (Ripple et al., 2001, White et al., 2003). However, resources available to aspen provide the energetic.

Wolf Essential TShirt by FluffyTheDude T shirt, Shirts, Anime shirt
Small-mammal specimens separated by 30 years and wolf spiders from short-term warming experiments show similar patterns of change, switching from plant-based to fungal-based food webs.

a painting of a wolf with yellow eyes and green leaves around it's neck
Wolf elk, mule deer, bison Coyote scavenger: will eat almost anything animal or vegetable; prefers rodents, rabbits Using the above data chart, create a food web: • Cut out each of the organism pictures and glue onto large paper. • Draw arrows that show the flow of energy. (Arrow goes to the eating animal)

an artistic photo of a wolf with feathers on it's head and the image of
Small-mammal specimens separated by 30 years and wolf spiders from short-term warming experiments show similar patterns of change, switching from plant-based to fungal-based food webs. Philip J.

Abstract vector illustration of wolf head in front Stock Vector
Wolves and the Food Web. Wolves play a very important role in the ecosystems they inhabit affecting not only prey population and health, but impacting everything from the trees and streams to the birds singing in the trees. When wolves are removed, their role as ecosystem engineers cannot be easily replaced. November 9, 2023.

Pin de Didier Moscot em Guardado rápido Desenhos pequenos para
The wolf is a large carnivore whose main prey are large, hooved herbivores such as the moose, elk and deer that scientists call ungulates. Unlike several species of cat, which eat only meat (hypercarnivores), wolves have adapted to eating a more varied diet; they are generalists and opportunistic hunters. While ungulates are wolves' primary.

Little wolf Picture of a wolf pup living in the zoo of Zür… Flickr
Vocabulary. A food web is all of the interactions between the species within a community that involve the transfer of energy through consumption. A food web incorporates different food chains within an environment. These types of interactions occur between producer and consumer, and between predator and prey. The transfer of energy starts with.

a black and white drawing of a wolf with his mouth open, showing the teeth
They construct and analyze a food web for Yellowstone National Park. Finally, students use what they have learned to better understand the trophic cascade caused by the return of wolves to Yellowstone. This learning activity provides an introduction to the learning activities, Carbon Cycles and Energy Flow through Ecosystems and the Biosphere.

a drawing of a wolf with feathers on it's head and another animal in
Red Wolf Food Web and Food Chain Red wolves are smaller than grey wolves and are on the endangered species list. In 1973, a restorative breeding program was established at the Point Defiance Zoo.

Food Web Red Wolf Food Chain Transparent PNG 1437x1139 Free
We created a series of conceptual models to depict the functional components of the wolf → elk → aspen food web (Fig. 1).Many more food web components would be possible, if one were to build an interaction web model for this system (Lavigne, 1995).To represent bottom-up forces, we included Environment (e.g., moisture) and Disturbance (e.g., fire, flooding, and insect outbreaks).