
MowatWilson syndrome Atlas of Human Malformation Syndromes in Diverse Populations
Mowat-Wilson syndrome is a genetic condition that affects many parts of the body. Major signs of this disorder frequently include distinctive facial features, intellectual disability, delayed development, an intestinal disorder called Hirschsprung disease, and other birth defects.

img_6376 MowatWilson Syndrome Foundation
Mowat-Wilson syndrome (MOWS) is an autosomal dominant complex developmental disorder; individuals with functional null mutations present with impaired intellectual development, delayed motor development, epilepsy, and a wide spectrum of clinically heterogeneous features suggestive of neurocristopathies at the cephalic, cardiac, and vagal levels.
Living with MowatWilson syndrome Rare Disease Day 2024
Purpose: Mowat-Wilson syndrome (MWS) is a genetic disease characterized by distinctive facial features, moderate to severe intellectual disability, and congenital malformations, including Hirschsprung disease, genital and eye anomalies, and congenital heart defects, caused by haploinsufficiency of the ZEB2 gene. To date, no characteristic pattern of brain dysmorphology in MWS has been defined.

IMG_5361 MowatWilson Syndrome Foundation
Mowat-Wilson syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that was clinically delineated by David R. Mowat and Meredith J. Wilson in 1998. [1] [2] The condition affects both males and females, has been described in various countries and ethnic groups around the world, and occurs in approximately 1 in 50,000-100,000 births. [3] Presentation
MWSRare2019AmeliaK MowatWilson Syndrome Foundation
Mowat-Wilson syndrome is an established intellectual disability/multiple congenital anomaly syndrome, characterized by typical facies, severe intellectual disability (ID), epilepsy, and variable congenital malformations including Hirschsprung disease, congenital heart disease, urogenital anomalies (hypospadias), and agenesis of the corpus callosum.
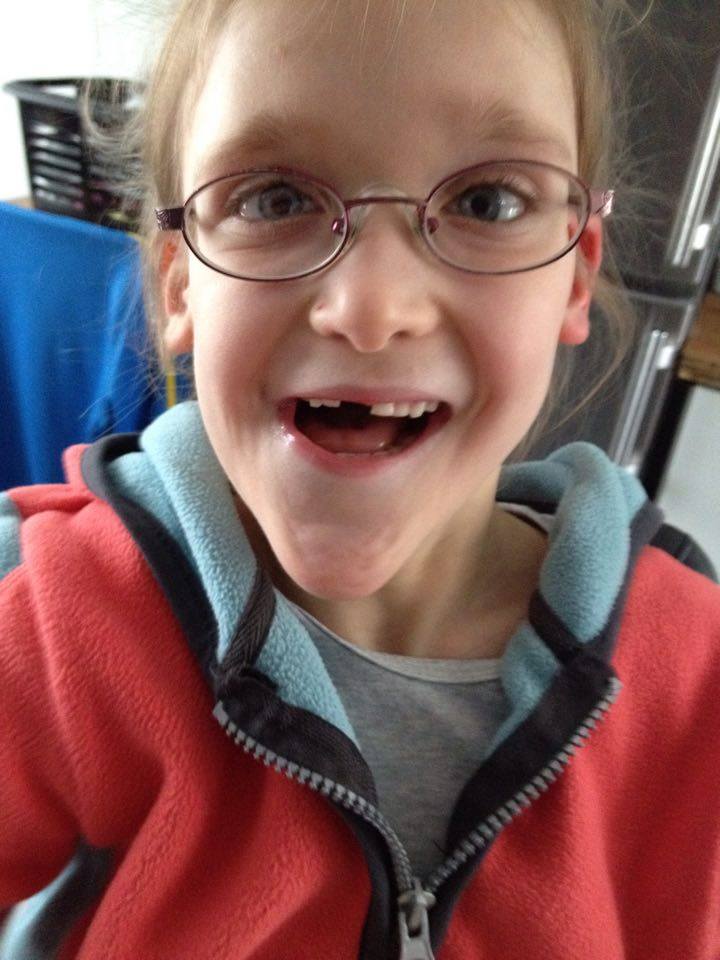

Living With MWS MowatWilson Syndrome Foundation
Clinical characteristics: Mowat-Wilson syndrome (MWS) is characterized by distinctive facial features (widely spaced eyes, broad eyebrows with a medial flare, low-hanging columella, prominent or pointed chin, open-mouth expression, and uplifted earlobes with a central depression), congenital heart defects with predilection for abnormalities of t.

Official Video About MowatWilson Syndrome MowatWilson Syndrome Foundation
Mowat-Wilson syndrome (MWS) is a rare genetic disorder that may be apparent at birth or later in childhood. MWS is characterized by intellectual disability, distinctive facial features and seizures.

MWSRare2019LennonT MowatWilson Syndrome Foundation
Mowat-Wilson syndrome (MWS) is characterized by distinctive facial features (widely spaced eyes, broad eyebrows with a medial flare, low-hanging columella, prominent or pointed chin, open-mouth expression, and uplifted earlobes with a central depression), congenital heart defects with predilection for abnormalities of the pulmonary arteries and/.

Novel Zeb2 gene variation in the Mowat Wilson syndrome (MWS) Journal of Pediatric Surgery
Mowat-Wilson Syndrome (MWS) (OMIM # 235730) is a rare disorder due to ZEB2 gene defects (heterozygous mutation or deletion). The ZEB2 gene is a widely expressed regulatory gene, extremely important for the proper prenatal development.

Mowat Wilson Sendromu Nedir?Belirtileri, Nedenleri,Tanısı ve Tedavisi
Research. Support. Hope. Our mission is to enhance the lives of people affected by Mowat-Wilson Syndrome Family Support + Raise Awareness + Research A community of support for rare, special children and their families DONATE TODAY! LATEST NEWS FROM THE MOWAT-WILSON SYNDROME FOUNDATION November/December 2023 MWSF Newsletter Read more

MWSRare2019JuanN2 MowatWilson Syndrome Foundation
Mowat-Wilson syndrome (MWS) is a multiple congenital anomaly syndrome characterized by a distinct facial phenotype (high forehead, frontal bossing, large eyebrows, medially flaring and sparse in the middle part, hypertelorism, deep set but large eyes, large and uplifted ear lobes, with a central depression, saddle nose with prominent rounded nasal tip, prominent columella, open mouth, with M.

MowatWilson syndrome Journal of Medical
Mowat-Wilson syndrome clinically tends to present as: Prominent Facial features: a square-shaped face with deep-set, widely spaced eyes, broad nasal bridge with a rounded nasal tip; a prominent and pointed chin; large, flaring eyebrows; and uplifted earlobes with a dimple in the middle. Affected people tend to have a smiling, open-mouthed.

Register to the Registry MowatWilson Syndrome Foundation
Ocular Features: Most reports of Mowat-Wilson disorders provide only incomplete ocular findings and the full phenotype remains to be described. Most of the reported findings are part of the facial phenotype, such as downward slanting palpebral fissures, and 'wedge-shaped' eyebrows with the medial portion visibly wider than the temporal region.
Living With MWS MowatWilson Syndrome Foundation
Mowat-Wilson syndrome is a genetic condition that affects many parts of the body. Major signs of this disorder frequently include distinctive facial features, intellectual disability, delayed development, an intestinal disorder called Hirschsprung disease, and other birth defects.

Living With MWS MowatWilson Syndrome Foundation
Mowat-Wilson syndrome is a genetic condition that affects many parts of the body. Major signs of this disorder frequently include distinctive facial features, intellectual disability, delayed development, an intestinal disorder called Hirschsprung disease, and other birth defects. Children with Mowat-Wilson syndrome have a square-shaped face.

Logan MowatWilson Syndrome Foundation
Mowat-Wilson syndrome (MWS; OMIM #235730) is a genetic condition caused by heterozygous mutations or deletions of the ZEB2 gene. It is characterized by moderate-severe intellectual disability, epilepsy, Hirschsprung disease and multiple organ malformations of which congenital heart defects and urogenital anomalies are the most frequent ones.